Kristi Sharma, M.Optom
Education Engagement Manager, Vision Science Academy
Synopsis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionising the field of ophthalmology, offering tools that augment the capabilities of eye care professionals in academic and research settings. Rather than supplanting human expertise, AI serves as a collaborative partner enhancing diagnostic accuracy, streamlining workflows, and expanding educational resources. This synergy ensures that eye care providers remain at the forefront of patient care, education, and scientific discovery, with total efficiency in all aspects.
Advancing Academic Excellence
AI has emerged as an important inclusion in the academic prospects.(1) It has helped bring to use specialised tools for learning, streamlining and enhancing learning through collaboration.
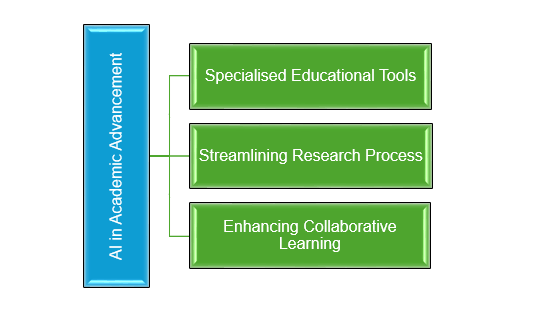
Image 1. Role of AI in Academics
- Specialised Educational Tools
AI driven platforms are tailored to the ophthalmic domain, providing interactive learning experiences for students and professionals alike. These tools stimulate clinical scenarios, offer instant feedback, and adapt to individual learning curves, thereby enriching the educational landscape.(1,2)
- Streamlining Research Processes
In research, AI accelerates data analysis by efficiently processing large datasets, identifying patterns, and generating hypotheses. For instance, AI algorithms have been developed to analyse retinal images, aiding in the early detection of conditions like diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. Such capabilities not only expedite research timelines, but also open new avenues for exploration.(1,2)
- Enhancing Collaborative Learning
AI facilitates global collaboration by providing platforms where professionals can share data, insights, and methodologies. This inter-connectedness fosters a community of continuous learning and innovation, essential for advancing ophthalmic research and practice.(1,2)
Augmenting Clinical Research
AI also has the ability to assist in the methodology of clinical research, the most time-consuming and labour-intensive part of any research.(1-3) Data collection and analysis can be eased with the help of AI integration in the research procedure.
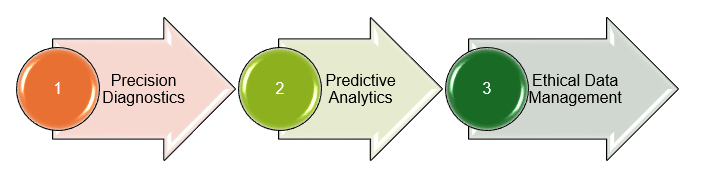
Image 2. Role of AI in Clinical Research
- Precision Diagnostics
AI systems have demonstrated proficiency in diagnosing various eye conditions. With high sensitivity and specificity rates of these AI systems, these tools have guided in the early detection and treatment planning, enhancing patient outcomes.(4)
- Predictive Analytics
Beyond diagnostics, AI offers predictive insights by analysing trends and risk factors. This capability enables researchers to anticipate disease progression and evaluate the potential impact of interventions, thereby informing clinical trials and public health strategies.(5)
- Ethical Data Management
AI aids in maintaining ethical standards by anonymising patient data and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations. This function is crucial in research settings, where data security and patient confidentiality are paramount.(6)
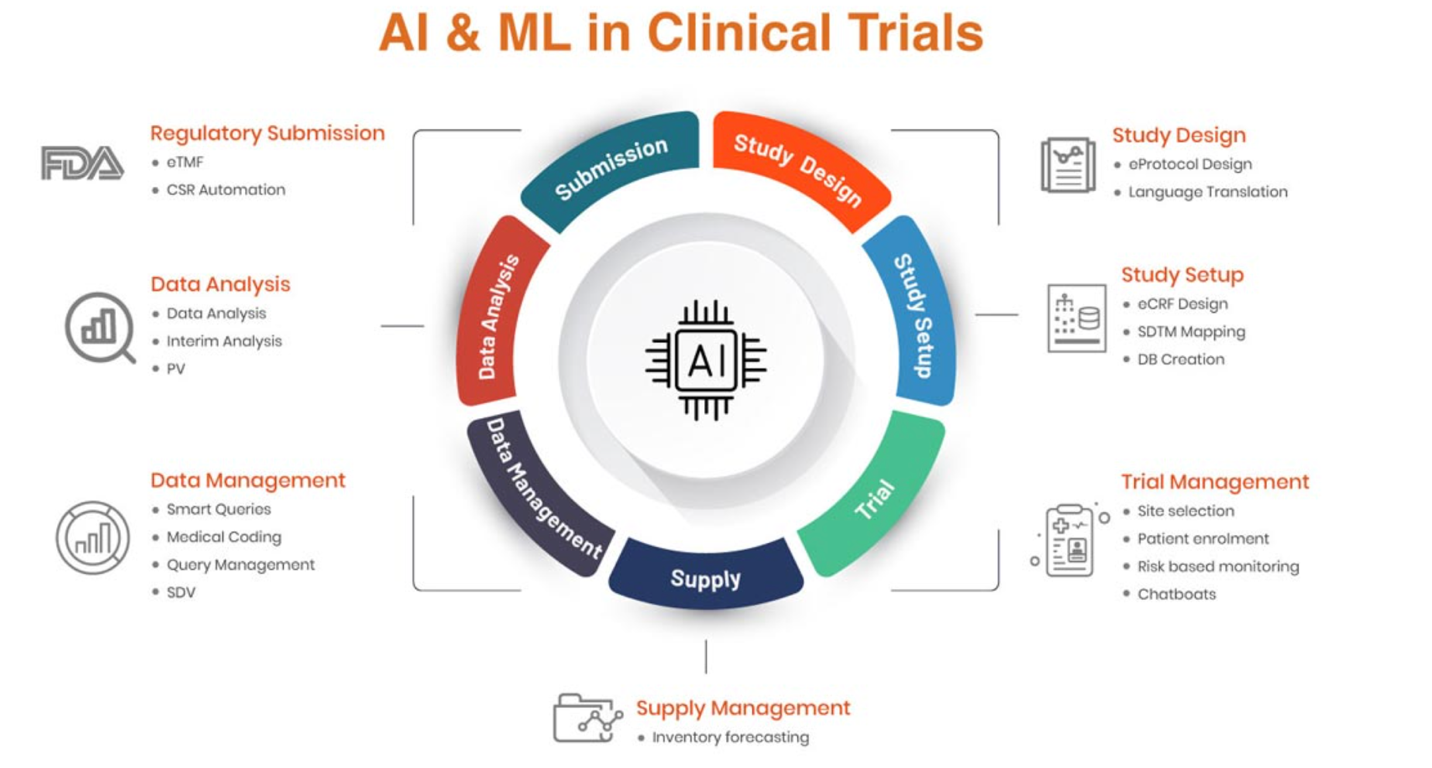
Image 3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Clinical Trials
Image Courtesy: Manuj Vangipurapu. Clinion. https://www.clinion.com/insight/ai-and-automation-in-clinical-trials/
Supporting Medical Education
Over the last decade, there has been significant improvement in using Augmented Reality (AR) in several mainstream fields like automotive industries, healthcare, gaming, production, and tourism. In the recent past AR technology has been paired with headsets which offer immersive experience of the surrounding environment. These headsets are now being replaced by smart glasses making them less cumbersome and more discreet.
Supporting, Not Replacing
Although numerous benefits are offered by AI, its integration necessitates careful considerations on data privacy, clinical judgement to always check and not blindly trust AI inputs, as well as maintaining continuous training with diverse and updated datasets to maintain accuracy and relevance in dynamic clinical environments. AI serves as an adjunct to human expertise, handling repetitive tasks which allows professionals to focus on complex decision making.(8) This collaboration enhances efficiency without compromising human touch essential in healthcare practice and research advancements. AI systems learn from ongoing data inputs, adapting to new information and evolving medical guidelines. This dynamic learning process supports professionals in staying updated with the latest advancements and best practices.(8)
Efforts are underway to ensure AI systems are trained on diverse datasets, minimising biases and promoting equitable care across different populations. Such initiatives underscore the commitment to inclusiveness and fairness in AI applications.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into eye-care signifies a transformative era where technology and human expertise converge to elevate patient care, education and research. By embracing AI as a collaborative tool, eye care professionals can enhance their capabilities, drive innovation, and continue to lead in delivering exceptional healthcare.
References:
- Heinke, A., Radgoudarzi, N., Huang, B. B., & Baxter, S. L. (2024). A review of ophthalmology education in the era of generative artificial intelligence. Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology, 100089.
- Valikodath, N. G., Cole, E., Ting, D. S., Campbell, J. P., Pasquale, L. R., Chiang, M. F., & Chan, R. P. (2021). Impact of artificial intelligence on medical education in ophthalmology. Translational Vision Science & Technology, 10(7), 14-14.
- Bakshi, S. K., Lin, S. R., Ting, D. S. W., Chiang, M. F., & Chodosh, J. (2021). The era of artificial intelligence and virtual reality: transforming surgical education in ophthalmology. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 105(10), 1325-1328.
- Chaudhari, G., Suryawanshi, S., & Chaudhari, S. (2024). AI-driven diagnostics: Transforming medical imaging with precision, efficiency and enhanced clinical accuracy.
- Betzler, B. K., Rim, T. H., Sabanayagam, C., & Cheng, C. Y. (2022). Artificial intelligence in predicting systemic parameters and diseases from ophthalmic imaging. Frontiers in Digital Health, 4, 889445.
- Kazemzadeh, K. (2025). Artificial intelligence in ophthalmology: opportunities, challenges, and ethical considerations. Medical hypothesis discovery and innovation in ophthalmology, 14(1), 255-265.
- Gurnani, B., & Kaur, K. (2024). Leveraging ChatGPT for ophthalmic education: A critical appraisal. European Journal of Ophthalmology, 34(2), 323-327
- Jiang, Y., Jiang, H., Yang, Z., Li, Y., & Chen, Y. (2024). The application of novel techniques in ophthalmology education. Frontiers in Medicine, 11, 1459097.